Need shorter lead time? Lead time of uncoated DOE is 5 weeks shorter! Click here for questions.
| Period [um] | Lines/mm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 666.667 | |||||||
| 2 | 500.000 | |||||||
| 2.5 | 400.000 | |||||||
| 3 | 333.333 | |||||||
| 3.5 | 285.714 | |||||||
| 4 | 250.000 | |||||||
| 6 | 166.667 | |||||||
| 6.65 | 150.376 | |||||||
| 8 | 125.000 | |||||||
| 11.25 | 88.889 | |||||||
| 11.85 | 84.388 | |||||||
| 12 | 83.333 | |||||||
| 14 | 71.429 | |||||||
| 14.1 | 70.922 | |||||||
| 16 | 62.500 | |||||||
| 16.7 | 59.880 | |||||||
| 18 | 55.556 | |||||||
| 19 | 52.632 | |||||||
| 21.5 | 46.512 | |||||||
| 22.5 | 44.444 | |||||||
| 24 | 41.667 | |||||||
| 25 | 40.000 | |||||||
| 25.75 | 38.835 | |||||||
| 27 | 37.037 | |||||||
| 29.5 | 33.898 | |||||||
| 33.25 | 30.075 | |||||||
| 34 | 29.412 | |||||||
| 36 | 27.778 | |||||||
| 38 | 26.316 | |||||||
| 39 | 25.641 | |||||||
| 40 | 25.000 | |||||||
| 42 | 23.810 | |||||||
| 45 | 22.222 | |||||||
| 47 | 21.277 | |||||||
| 48 | 20.833 | |||||||
| 50 | 20.000 | |||||||
| 56 | 17.857 | |||||||
| 61 | 16.393 | |||||||
| 68.125 | 14.679 | |||||||
| 80 | 12.500 | |||||||
| 86 | 11.628 | |||||||
| 90.375 | 11.065 | |||||||
| 115.75 | 8.639 | |||||||
| 127.5 | 7.843 | |||||||
| 132.5 | 7.547 | |||||||
| 180 | 5.556 | |||||||
| 225 | 4.444 | |||||||
| 243 | 4.115 | |||||||
| 269.5 | 3.711 | |||||||
| 300 | 3.333 | |||||||
| 350 | 2.857 | |||||||
| 415 | 2.410 | |||||||
| 448.85 | 2.228 | |||||||
| 450 | 2.222 | |||||||
| 478.25 | 2.091 | |||||||
| 532 | 1.880 | |||||||
| 673.125 | 1.486 | |||||||
| 800 | 1.250 | |||||||
| 830 | 1.205 | |||||||
| 847.875 | 1.179 | |||||||
| 848 | 1.179 | |||||||
| 890 | 1.124 | |||||||
| 1230 | 0.813 | |||||||
| 1598 | 0.626 | |||||||
| 1907 | 0.524 | |||||||
| 2308 | 0.433 | |||||||
| 2336 | 0.428 | |||||||
| 2640.5 | 0.379 | |||||||
| 2660 | 0.376 | |||||||
| 3167.5 | 0.316 | |||||||
| 3231 | 0.310 | |||||||
| 3869 | 0.258 | |||||||
Need shorter lead time? Lead time of uncoated DOE is 4 weeks shorter!Click here for RFQ and questions | ||||||||
Loading, Please Wait...
For DOE solutions outside this range, please contact us for custom solutions.
| Materials | Fused Silica, ZnSe, Germanium, Plastic |
|---|---|
| Wavelength range | 193nm to 10.6um |
| DOE design | 2-level (binary) |
| Separation angle | Smaller than 80deg @ 1064nm |
| Diffraction efficiency | 81% (theoretically) |
| Element size | Few mm to 150mm |
| Coating (optional) | AR/AR Coating |
| Custom Design | Custom duty cycle, period and modulation depth |
Features:
What is a Phase Diffraction Grating?
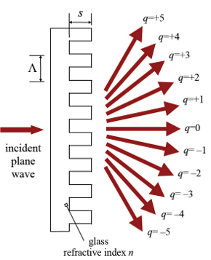
A phase grating is a transmissive window with one surface having a periodic modulation in phase. Such modulation creates a diffraction effect on coherent light going through the grating, resulting in the splitting of the input beam into multiple out beams, called orders. each beam has the same characteristics as the input beam, and an output angle determined by the order number .
The relationship between the angles of the order, the order number and the period is known as the grating equation, as seen in the calculator in this page.
Types of Diffraction Gratings
Simple binary diffractive gratings, offered in this page, have the most energy in the first two orders (+-1), while more complex periodic gratings can generate energy distributions that allocate most of the input laser energy equally to a desired number of output orders. These are often called Damman gratings or Fan out gratings.
By creating surface structures that are periodic in both x and y, i.e made of cells that are replicated over the entire surface, custom diffraction gratings can also split the light to two-dimensional beam arrays.
In Holo/OR , you can find these types of gratings in our 1D and 2D beam splitter pages. This page is aimed at binary gratings with duty cycle 50:50, though other options are possible if desired.
Key features of Holo/Or Diffraction Gratings
- Absolutely accurate angle of separation
- High Laser Damage Threshold
- Fused Silica or ZnSe Material
- Custom duty cycle, period and modulation depth
- Wavelengths from DUV 193nm to IR 10600nm
- Optional AR/AR coating for transmissive gratings or HR coating for reflection mode gratings.
Holo/Or Gratings manufacturing method
All Holo/Or binary diffraction gratings are produced using a precise lithography and plasma etching method, resulting in excellent phase height accuracy and sharp side wall slope.
FAQ
Q:What is the Difference between a phase diffraction grating and an amplitude grating ?
A: Phase gratings have ~100% transmission an no absorption, making them suitable for high power lasers and precise applications. Amplitude grating work by absorption thus have ~40% efficiency and are better for low end applications.
Q:How does groove depth affect diffraction grating performance?
A: Holo/Or gratings groove depths are optimized for a design wavelength, with good efficiency (80% to orders +-1) at a bandwidth of +-2% around this wavelength. longer wavelengths require deeper groove depth, accordingly, but this has no bearing on cost of performance for our binary grating products.
Q:Can diffraction gratings be optimized for different wavelengths?
A: Yes, by modifying groove depth, as described above.
Q:How do I choose the right diffraction grating for my application?
A: Diffraction gratings with high line density have larger angles, thus enable a broader spectrum on a given sensor. However, spectral resolution is a trade-off , as it is decreased with increasing density. Lower density gratings with longer periods offer better sensitivity over narrower spectrums.
Applications:
- Spectroscopy – Used for precise wavelength separation.
- Optical Metrology – used to define precise separations on an image for calibration
- Industrial Laser monitoring- Helps control beam reflections and improve system efficiency
- Parallel material processing
- Microscopy – Essential in wavelength dependent medical imaging.