Diffractive optical elements are widely used in infrared systems, especially where industrial processes are involved. This article focuses on laser welding application and showcases unique custom solutions which provide competitive advantage to the systems using them
Infrared lasers trends
Infrared lasers, especially in the 1um wavelength region, are the workhorses of the laser material processing industry. The first industrial lasers were CO2 mid-IR lasers, that have been gradually replaced in many applications with ND-YAG solid state lasers, and recently, fiber lasers. The rapidly increasing power and decreasing cost of multi-kW lasers is making them ubiques in many industrial processes such as welding, cutting, sintering and surface treatment.
This article will focus on Laser welding, which is one case study for high-powered NIR lasers applications.
Introduction to laser welding
Laser welding is used in a wide range of industrial applications including automotive, aerospace, semiconductors, electronics, medical, power, defense, and others. Compared to other laser material processing applications, these processes stand out in terms of the required laser power (multi kW) and typically used IR lasers.
For many industrial applications and processes the raw laser beam is not the optimal shape. In the field of welding, brazing, soldering, and other similar processes, shaping the laser beam into a process-specific tailored intensity distribution can offer a valuable advantage and improve process properties, some of which include:
- Throughput
- Seam height
- Strength
- Edge smoothness of the joints
While helping avoid unfavorable effects, such as heat affected zones (HAZ), spattering, humping and weld porosity.
Diffractive optical elements present a simple, cost effective, robust and easy to integrate solution for many of these cases.
Diffractive Optical Element Basics
Diffractive optical elements (DOEs) are flat, window-like phase elements which use micro structures etched into the surface of the element in order to create a phase delay in a potion of the light which is illuminated through the element, and thus modify the output beam.
A well thought of diffractive optical element design can shape the beam into almost any desired intensity profile from splitting the beam to multiple beams sharing similar characteristics as the input beam to flat-top distributions at any desired geometrical distribution, ring shapes or focal shaping, and even combine multiple functionalities on the same optical element to provide custom tailored solutions.
Holo/Or was the first diffractive optical element manufacturer, who offered to apply microelectronics fabrication processes to optical elements for commercial applications back in the late 1980’s. Since then, the diffractive optical elements market grew and today a huge variety of laser applications enjoy the benefits they can provide.
In the case of diffractive optical elements for use in infrared systems, the DOE will be fabricated on a material which is transparent to the IR spectrum to allow high transmission efficiency and to eliminate absorption which can heat up the element, causing defects which will degrade its functionality. The anti-reflection (AR) coating is also of high quality to sustain the high IR power.
Customized diffractive optical elements for laser welding applications
Several different fixed and adjustable DOE solutions for laser welding are offered by HOLO/OR including:
- Flexishaper – An innovative solution combined of 2 DOEs enabling an adjustable ring to spot ratio of the energy from a standard fiber laser, with a simple rotation of one of the DOEs against the other. This unique solution can be applied to both single mode and multimode laser systems to find the optimal working point per process.

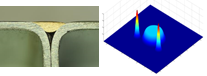
- C-shaper – A custom diffuser shape which allows nitrogen bubbles a place to escape the weld area and thus improve width/depth ratio, reduce oxidation and eliminate hot cracking.

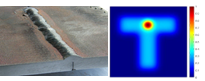
- T-shaper – An optimal solution for butt-joint welding which enables scanning the shape along the weld seam with hot spot in the center and thus improve post-weld annealing, reduce weld seam angle and improve weld strength
- Brazing Diffuser – A combined beam splitter and diffuser which generates 2 leading spots and one center spot, which when scanned during a brazing process melts the wire between the two plates, while preheating and cleaning both sides of the brazed seam.
TL; DR - Q&A
What is diffractive optical element?
A thin, compact and robust optical element which manipulates light for shaping, splitting and focusing purposes.
What is a diffractive optical lens?
A compact, thin window which functions the same way as a conventional refractive lens for the design wavelength, but is much thinner and possess much less thermal expansion.
What are the advantages of diffractive optical elements for use in infrared systems?
DOEs enable shaping the light in precise high-end applications while having low heat absorption and extremely low thermal expansion relative to refractive solutions, and are made of materials that can withstand very high power as is used in many IR laser systems.
What customized solutions do diffractive optical element designs have for laser welding?
Transforming the laser profile into a C shape intensity profile can reduce oxidation and eliminate hot cracking. Another solution is a DOE variable ring and spot intensity profile which can be achieved without the need to change the laser construction.

