Fractional treatments in dermatology use laser spots array on a patient’s skin for optimal process. The article presents approaches to generate spots array
Background: Laser fractional treatment
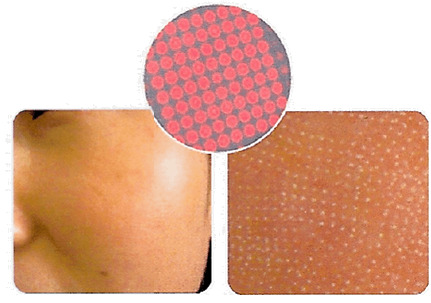
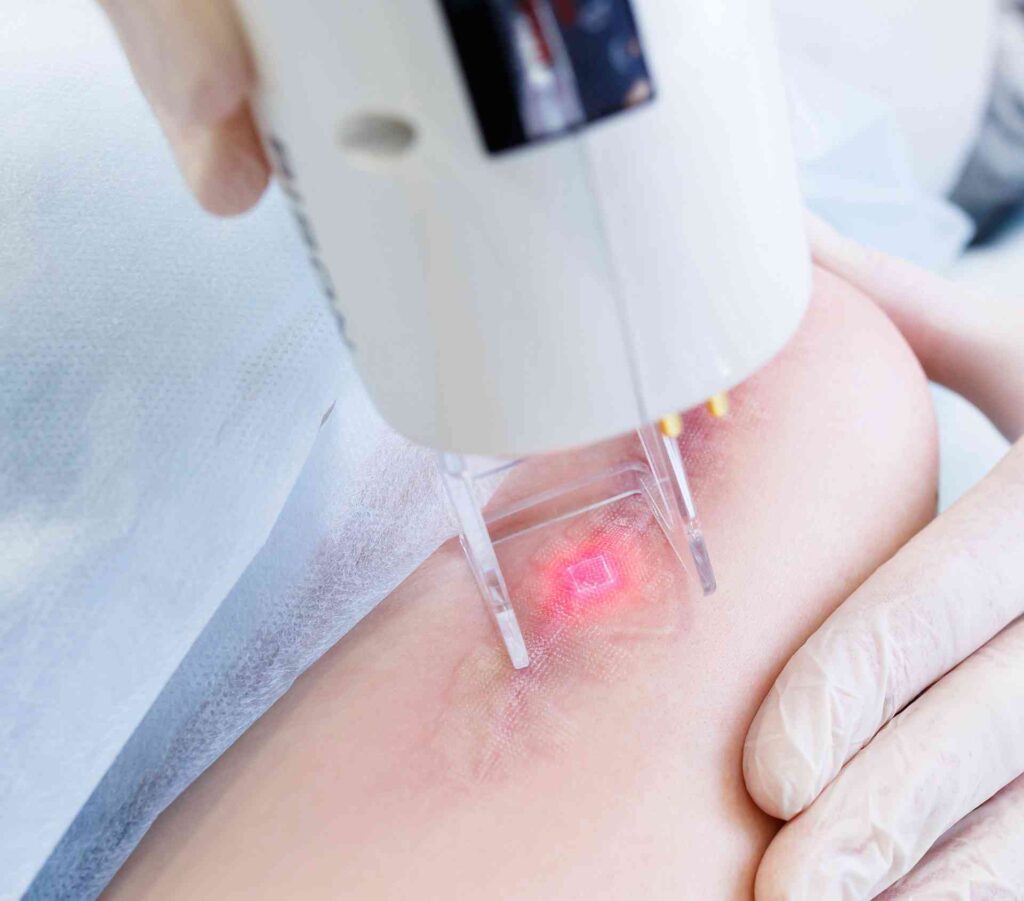
Fractional laser aesthetic treatments are a family of laser processes conducted with Energy Based Devices (EBDs) that rejuvenate the skin by careful, controlled application of laser energy over thousands of individual spots, often called micro-thermal treatments zones. To achieve this pattern of spots on the skin, the laser energy needs to be either rapidly scanned from spot to spot, or divided into an array of beams, or some combination of the two.
Fractional laser treatment was first been developed in 2004, and have since become one of the most sought-after aesthetic treatments. Various laser wavelengths are used in fractional treatments, from MIR (CO2 lasers and erbium-YAG) to short pulse NIR and even VIS (Nd-YAG lasers at nano or pico-second regime pulses at 1064nm, 532nm).
Laser beam shaping approaches for fractional treatment
As described above, there are three main approaches to achieving the pattern of spots on the patients’ skin:
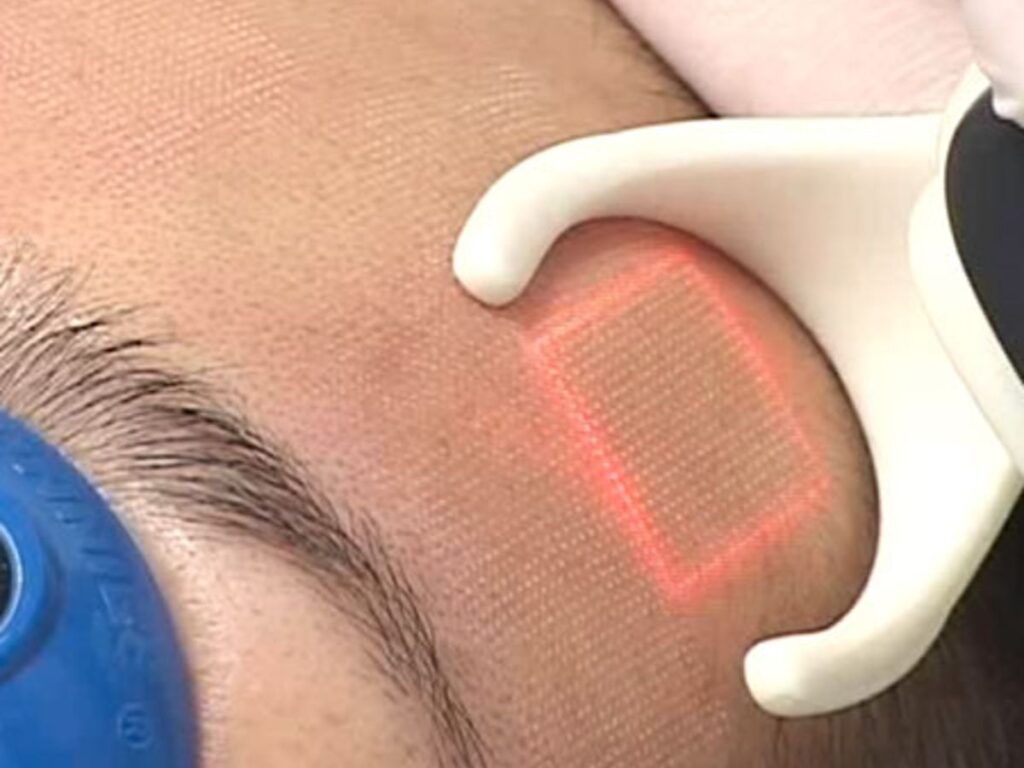
- Using a micro scanner mounted in the handle to steer the beam spot-by spot over the entire field (i.e., both in x and Y direction). The handle is moved over the skin with the scanner generating the pattern, but stitching of treated areas is done manually.
- Splitting the beam into an array of spots. This is often done using a diffractive optical element, called a diffractive beam splitter, to split the laser beam into an array of spots with well-defined separations. The array is often symmetrical (9X9 spots, 7X7 spots and others) and covers a small area. The treatment is performed by moving the handpiece to cover new areas and stitching the treated areas manually. Another option which is sometimes used to generate the pattern of spots is a micro lens array, that works by a refractive rather than a diffractive method.
- Using a combination of a one-dimensional diffractive beam splitter and a 1D scanner to generate the matrix of dot. This combines the flexibility of the scanner approach (treatment area shape can be changed) with the robustness of the diffractive beam splitter approach (scanning can be done only in a single axis, making the scanner simpler and cheaper and the process more robust).
Diffractive optical elements advantages in fractional laser skin treatments
The splitting of a beam into an array of spots can be done by either a micro lens array or a diffractive optical element. The DOE optics approach has several advantages:
- Uniformity: The type of DOE used in fractional treatments is designed using digital diffractive optics optimization methods to give a uniform distribution of the spots, regardless of the laser input distribution. Each spot is exactly the same as the input spot. That is not the case with a micro lens array, where each spot is created by a sub-aperture, and the spots intensities have the same gaussian envelope as the input beam profile. Often this means that when using a micro lens array, the laser must be homogenized and passed through an aperture or multimode fiber which reduces efficiency.
- Accuracy: Diffractive optical components produced by Holo/Or have no tolerance on their separation angle, as they are produced by lithographic methods. All spots are focused by a single external lens to the same plane. In contrast, a micro lens array has a tolerance on lens ROC, resulting in changes to spot diameters due to different defocus.
- Shaping flexibility: A diffractive beam splitter can be combined with other shaping functions, such as homogenization to reduce hot spots which can harm a patient’s skin and other optical components in the device (multi-mode lasers used in aesthetic laser treatments often have less stable beam profiles).
TL;DR - Q&A summary
WHAT ARE FRACTIONAL LASER TREATMENTS IN AESTHETIC MEDICINE?
Fractional laser treatments are laser treatments with Energy Based Devices (EBD) where the laser energy is spread over the patient skin in the form of multiple spots, each having a fraction of the full laser energy. This has been shown to rejuvenate the skin, reduce wrinkles, treat pigmentation and other skin conditions.
WHAT TYPES OF LASER BEAM SHAPERS ARE USED IN FRACTIONAL LASER TREATMENTS?
In general, there are two main approaches: active scanning, where the beam is scanned point by point, and passive splitting, where the beam is split to an array of spots using a diffractive beam splitter or micro lens array.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF DIFFRACTIVE BEAM SPLITTERS FOR FRACTIONAL LASER TREATMENTS?
Diffractive optical elements have no angular tolerance, ensuring absolute accuracy of the spots relative positions, and excellent spot uniformity, while also allowing adding other shaping functions to the diffractive beam splitter, such as homogenization of the spots, all on a single surface.

